Home > News > Industry News > A Guide to Choosing the Right Gauge: Stainless Steel Needles from 8G to 32G
A Guide to Choosing the Right Gauge: Stainless Steel Needles from 8G to 32G
Introduction
When it comes to precision adhesive dispensing, choosing the right needle gauge is one of the most critical decisions manufacturers face. Whether in electronics assembly, medical device manufacturing, automotive production, or research laboratories, adhesive must be dispensed accurately, consistently, and safely. A mismatch between the glue’s viscosity and the needle gauge can result in clogged needles, excessive flow, or uneven application.
That's why stainless steel blunt-tip dispensing needles—such as those developed by Contriu Technology—are widely trusted across industries. Manufactured with 304 stainless steel needle tubes, brass nickel-plated holders, and a secure bayonet base, these needles deliver unmatched durability and reliability. Even more importantly, they are available in gauges ranging from 8G to 32G, covering a wide spectrum of dispensing needs.
This guide explores how to select the right gauge, what each gauge size means in practice, and why Contriu’s stainless steel dispensing needles are the ideal choice for long-lasting precision.
What Does Needle Gauge Mean?
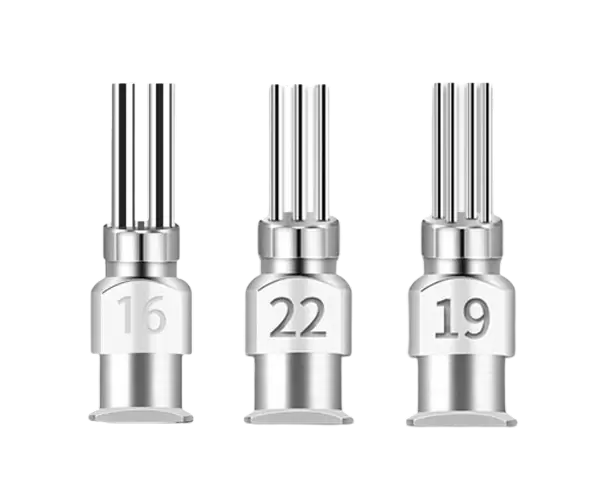
The gauge (G) of a dispensing needle refers to the internal diameter of the needle tube. It determines how much adhesive can pass through per unit of time. The system works in reverse:
A lower gauge number (e.g., 8G) indicates a larger diameter, allowing high-volume flow.
A higher gauge number (e.g., 32G) means a smaller diameter, suitable for micro-dispensing tasks.
For example:
8G–14G: Wide bore, ideal for high-viscosity adhesives like epoxies or silicones.
15G–22G: Medium range, suitable for general-purpose glues and sealants.
23G–32G: Fine bore, essential for microelectronics and delicate applications.
The Structure of Contriu’s Stainless Steel Needles
Before diving into gauge selection, let’s understand why Contriu Technology’s needles are particularly well-suited for industrial use:
Brass Nickel-Plated Needle Holder: Corrosion- and wear-resistant, ensuring secure connection and long-term reliability.
304 Stainless Steel Needle Tube: Provides high rigidity, chemical resistance, and burr-free precision machining.
Bayonet Base: Ensures a tight, leak-free fit with dispensing systems, preventing downtime.
Standard Lengths: 1/4 inch (6.5 mm), 1/2 inch (13 mm), 1 inch (25 mm), 1.5 inch (38 mm), with custom lengths available.
This construction ensures smooth, accurate adhesive flow across all gauge sizes, giving users confidence in high-precision environments.
A Breakdown of Gauges from 8G to 32G
8G–12G: For High-Viscosity Adhesives
These gauges are best suited for adhesives with very high viscosity, such as structural epoxies, silicones, or polyurethane sealants. The larger bore ensures uninterrupted flow without clogging. Industries like automotive and aerospace often rely on these gauges for sealing and bonding larger components.
13G–18G: Medium-High Flow Applications
These sizes work well with adhesives that are moderately thick but not overly viscous. They provide a balance between flow speed and control, making them common in industrial assembly lines where consistent bonding is required.
19G–24G: Versatile General Use
This range covers a broad spectrum of industrial needs, handling medium-viscosity adhesives like acrylics or UV-curable glues. These gauges are widely used in consumer electronics assembly, where consistent adhesive lines are essential for product quality.
25G–28G: Precision Work
These fine-gauge needles are crucial for micro-dispensing tasks. In industries like microelectronics, optics, and medical device assembly, tiny adhesive dots or lines must be applied without overflow. Stainless steel ensures stable flow, even with fine internal diameters.
29G–32G: Ultra-Fine Applications
The smallest gauges are reserved for the most delicate work, such as semiconductor manufacturing, optical lens bonding, or microfluidic device assembly. They allow adhesives to be dispensed in sub-microliter quantities, ensuring pinpoint accuracy.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Gauge
Viscosity of the Adhesive
High-viscosity = lower gauge (larger bore).
Low-viscosity = higher gauge (smaller bore).
Application Type
Large bonding surfaces → lower gauge.
Micro components → higher gauge.
Dispensing Pressure
Higher pressure can compensate for smaller gauges, but overpressure risks leaks.
Surface Sensitivity
Blunt-tip stainless steel prevents scratching fragile substrates, making fine gauges safer for electronics and optics.
Production Volume
High-speed production lines may prefer lower gauges for faster adhesive delivery.
Why Stainless Steel Is Ideal for All Gauges
Regardless of gauge, stainless steel offers advantages over plastic or aluminum alternatives:
Burr-Free Precision: Ensures clog-free operation even at ultra-fine gauges.
Corrosion Resistance: Compatible with aggressive adhesives.
Strength: Prevents bending or deformation at thin diameters.
Longevity: Reduces needle replacement frequency.
This makes stainless steel the only practical choice for gauges as fine as 32G, where accuracy is paramount.
Industry Applications of Gauge-Specific Needles
Automotive (8G–14G): Applying structural adhesives in body panels and seals.
Electronics (19G–28G): Circuit board bonding, microchip encapsulation, and solder masking.
Medical Devices (25G–32G): Catheter bonding, lens assembly, and implantable device adhesives.
Consumer Goods (13G–22G): Appliance assembly, packaging, and general adhesives.
Best Practices for Selecting and Using Gauges
Match needle gauge to adhesive viscosity—never force adhesives through undersized gauges.
Keep backup gauges on hand for different applications within the same production line.
Use custom lengths from Contriu when standard sizes don’t meet your setup needs.
Regularly inspect needles for wear or buildup, especially at fine gauges.
Clean thoroughly after use to maximize service life.
Why Choose Contriu Technology?
Contriu Technology’s stainless steel dispensing needles are engineered to meet the highest global manufacturing standards. Key benefits include:
ISO-quality production processes for consistent precision.
Custom gauge and length support, meeting unique client needs.
Full burr-free machining, ensuring smooth flow across all gauge sizes.
Global support and reliable supply chain, ensuring timely delivery.
Their commitment to innovation has made them a preferred partner for manufacturers across electronics, medical, automotive, and research industries.
Conclusion
Choosing the right needle gauge can mean the difference between smooth, consistent adhesive application and costly rework. By offering stainless steel dispensing needles from 8G to 32G, Contriu Technology provides solutions for every application—from high-viscosity structural bonding to ultra-fine microelectronics work.
Backed by durability, corrosion resistance, and burr-free precision machining, these needles deliver superior performance across industries. Whether you need a large bore for high flow or an ultra-fine gauge for micro-precision, stainless steel remains the gold standard—and Contriu Technology is at the forefront of delivering it.