Home > News > Industry News > Best Practices for Using & Maintaining Stainless Steel Glue Needles in Lab and Industrial Settings
Best Practices for Using & Maintaining Stainless Steel Glue Needles in Lab and Industrial Settings
In laboratory research, electronics assembly, and a wide range of industrial applications, precision adhesive dispensing is crucial. One of the most reliable tools for achieving accuracy and consistency is the stainless steel glue needle. These dispensing needles are designed to handle adhesives, sealants, and other viscous materials while providing control, durability, and chemical resistance. However, simply owning quality dispensing needles is not enough. Knowing how to use and maintain them properly ensures safety, accuracy, and longer service life.
In this article, we’ll explore the best practices for using and maintaining stainless steel glue needles in both laboratory and industrial environments. Whether you are assembling electronic components, applying adhesives in medical device production, or working in general manufacturing, these guidelines will help you maximize performance and minimize downtime.
Why Stainless Steel Glue Needles Matter
Stainless steel dispensing needles stand apart from their plastic counterparts due to their:
Durability: Resistant to bending and breakage under pressure.
Chemical resistance: Compatible with a wide range of adhesives and solvents.
Precision: Uniform inner diameters ensure consistent flow rates.
Versatility: Suitable for manual syringes, pneumatic dispensers, and automated dispensing systems.
Because of these advantages, stainless steel needles are widely used in industries like electronics, automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and laboratory R&D. For more details on specifications and options, see stainless steel glue needles here.
Best Practices for Using Stainless Steel Glue Needles
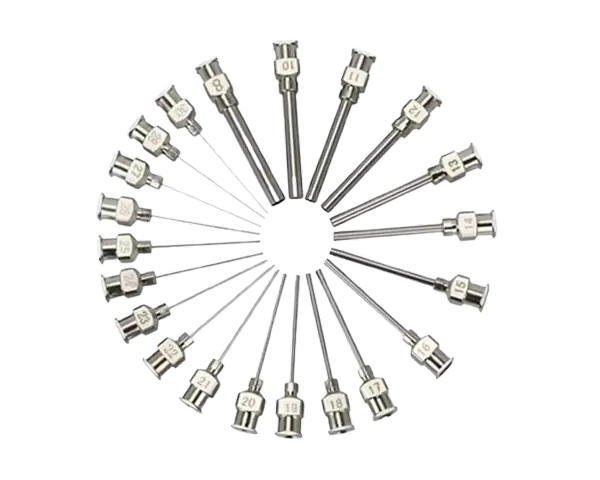
1. Choose the Right Needle Size
Selecting the correct needle gauge is the foundation of precise dispensing.
Fine gauge (small inner diameter): Best for thin adhesives, solvents, or micro-dispensing in electronics.
Medium gauge: Suitable for general-purpose gluing in industrial and lab use.
Large gauge (wider inner diameter): Ideal for high-viscosity adhesives, sealants, or large-volume dispensing.
Pro Tip: Always match the adhesive viscosity with the appropriate needle size. Using too fine a needle for thick adhesives can cause clogs and irregular flow.
2. Use With Compatible Dispensing Systems
Not all dispensing systems are the same. While many stainless steel glue needles are universal, ensure they are compatible with your syringes, cartridges, or automated dispensing machines.
Manual use: Ensure needles fit snugly to prevent leakage.
Pneumatic systems: Use needles with secure luer-lock fittings to handle pressure.
Automated systems: Calibrate dispensing robots for flow rate, pressure, and cycle time according to the needle diameter.
3. Avoid Excessive Pressure
Applying too much pneumatic or manual pressure can lead to:
Adhesive dripping or backflow.
Needle bending or damage.
Inconsistent glue patterns.
Instead, use controlled dispensing pressures tailored to the adhesive type. For very viscous materials, consider warming the adhesive slightly or using tapered dispensing tips designed for high-viscosity flow.
4. Practice Safe Handling
Even though glue needles are not sharp in the same way as medical needles, they can still cause injuries if mishandled. Follow these safety practices:
Always cap or cover needles when not in use.
Store in dedicated trays or holders to prevent accidental contact.
Train operators in proper handling and disposal procedures.
Maintenance Practices for Stainless Steel Glue Needles
1. Regular Cleaning
Adhesive residue is the most common cause of clogging. To extend needle life:
Flush immediately after use: Use a solvent compatible with the adhesive (e.g., isopropyl alcohol for many epoxies).
Ultrasonic cleaning: For precision lab applications, ultrasonic baths can remove hardened residues without damaging the needle.
Dry thoroughly: Prevent rust or contamination by ensuring needles are completely dry before storage.
2. Prevent Cross-Contamination
Using the same needle for different adhesives can compromise experiments or production quality. Best practices include:
Dedicate needles to specific adhesive types.
Label storage containers clearly.
If sharing needles is unavoidable, perform deep cleaning between uses.
3. Inspect Before Use
Even stainless steel can wear down over time. Inspect for:
Bent tips that can affect dispensing accuracy.
Corrosion (though rare, it can occur if incompatible cleaning solvents are used).
Clogs that remain even after cleaning.
Replace needles showing any signs of damage to maintain consistent quality.
4. Store Properly
Storage is often overlooked but critical:
Keep in a dry, dust-free environment.
Use capped protective cases.
Avoid high humidity areas to reduce risk of corrosion.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Adhesive Clogging
Use wider gauge needles for thicker adhesives.
Warm the adhesive (if manufacturer-approved).
Adopt routine cleaning protocols.
Inconsistent Flow
Check for bent or damaged needle tips.
Verify correct pressure settings.
Inspect dispensing system fittings for leaks.
Needle Wear & Tear
Rotate needle inventory to prevent overuse of specific ones.
Replace damaged needles promptly.
Invest in high-quality stainless steel needles from trusted suppliers.
Industry Applications
Electronics: Applying solder paste, epoxy, and flux for circuit board assembly.
Medical Device Manufacturing: Precision bonding of components requiring sterile, accurate adhesive application.
Automotive & Aerospace: Dispensing sealants, lubricants, and adhesives for critical parts.
Laboratories: Micro-dispensing for chemical research, assays, and diagnostics.
These industries rely on the repeatability and robustness of stainless steel glue needles, making them an indispensable tool for professionals.
External Best Practices & Resources
To further explore dispensing best practices, you may find these references useful:
Adhesive and Sealant Council (ASC)– industry resources on adhesives and applications.
Engineering Toolbo – practical guides on fluid flow and viscosity relevant to adhesive dispensing.
Conclusion
Stainless steel glue needles are essential components for precision adhesive dispensing in both laboratory and industrial settings. By choosing the right size, practicing safe handling, cleaning regularly, and storing correctly, you can ensure consistent results and prolong the lifespan of your dispensing equipment.
When quality and precision matter most, investing in durable and well-maintained stainless steel needles makes all the difference. For reliable options designed for diverse applications, explore Contriu stainless steel glue needles.